Class 5 Science Cleanliness and Hygiene
Atom, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic Class 12 NIOS Chemistry MCQ
NIOS Class 12
Atoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic Class 12 Chemistry NIOS
Chapter 1: Atoms, Molecules and Chemical Arithmetic
Scope of Chemistry
Chemistry is called the central science because it connects physics, biology, medicine, agriculture, and environmental science.
Health and Medicine
- Vaccines, antibiotics, and anesthesia revolutionized healthcare.
- Gene therapy is a breakthrough that repairs defective genes.
- Chemists design drugs with fewer side effects.
Energy and Environment
- Fossil fuels are finite – chemists explore solar, nuclear, and hydrogen-based energy.
- Solar cells and fuel cells can replace pollution-heavy fuels.
- Chemists help reduce greenhouse gases and air pollution.
Materials and Technology
- Development of polymers, ceramics, liquid crystals, adhesives, etc.
- Superconductors can eliminate energy loss during electricity transfer.
Food and Agriculture
- Fertilizers, pesticides, and irrigation chemicals increase crop yields.
- Genetically modified seeds improve resistance to pests and climate conditions.
Particulate Nature of Matter
Matter can be divided into smaller particles up to a limit. These smallest indivisible particles are called atoms.
- Leucippus and Democritus proposed the atomic theory around 440 B.C.
- Maharshi Kanad in India called these particles Parmanu.
Laws of Chemical Combinations
Law of Conservation of Mass
Antoine Lavoisier showed that:
“Mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.”
Example: Decomposition of Mercury (II) oxide gives mercury and oxygen, and total mass remains the same.
Law of Definite Proportions
Joseph Proust showed that a compound always contains the same elements in the same proportion by mass.
Example: Water is always H:O = 1:8 by mass, regardless of source.
Law of Multiple Proportions
When two elements form more than one compound, the masses of one element that combine with a fixed mass of the other are in simple whole number ratios.
Example: In CO and CO₂, oxygen combines with carbon in a 2:1 mass ratio.
Dalton’s Atomic Theory
- All matter is made of indivisible atoms.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass and properties.
- Atoms of different elements differ in mass and chemical behavior.
- Atoms combine in whole-number ratios to form compounds.
- Atoms are neither created nor destroyed during chemical changes.
What is an Atom?
The smallest particle of an element that retains its chemical properties.
What is a Molecule?
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms chemically bonded together.
Examples:
- Diatomic molecules: O2, H2, N2
- Polyatomic molecules: H2O, NH3, CH4
What is an Element?
A pure substance consisting of only one type of atom. Represented by symbols (H, O, Fe, etc.)
Definitions
- Atom: The smallest particle of an element with its chemical identity.
- Molecule: Group of atoms bonded together (e.g., H₂, CO₂).
- Element: Pure substance made of only one kind of atom.
SI Units
- Mass – kilogram (kg)
- Length – metre (m)
- Time – second (s)
- Temperature – kelvin (K)
- Amount of substance – mole (mol)
Mole Concept
To count particles at the atomic level, we use the concept of mole.
1 mole = 6.022 × 10²³ particles (atoms/molecules/ions)
Avogadro’s Constant
Avogadro’s constant (NA) = 6.022 × 10²³ mol⁻¹
- 1 mole of atoms = 6.022 × 10²³ atoms
- 1 mole of molecules = 6.022 × 10²³ molecules
Empirical and Molecular Formula
Empirical Formula
The simplest whole-number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound.
Example: CH is the empirical formula of benzene (C₆H₆).
Molecular Formula
The actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
Formula:
Molecular Formula = n × Empirical Formula
where n = (Molecular mass) / (Empirical formula mass)
Steps to Calculate Empirical Formula:
- Find % composition or mass of elements.
- Convert mass to moles (divide by atomic mass).
- Divide by smallest value to get simplest ratio.
- Write the empirical formula.
Molar Volume of a Gas
At standard temperature and pressure (STP = 0°C and 1 atm):
- 1 mole of any gas occupies 22.4 L.
- This is known as the molar volume.
Applications:
- To calculate volume from moles:
Volume = moles × 22.4 L - To calculate moles from volume:
Moles = volume / 22.4 L
Chemical Equations
What is a Chemical Equation?
A symbolic representation of a chemical reaction showing reactants and products.
Steps to Write & Balance an Equation:
- Write correct chemical formulas of all reactants and products.
- Balance atoms of each element on both sides.
- Use smallest whole-number coefficients.
Example:
Unbalanced: H₂ + O₂ → H₂O
Balanced: 2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
⚖️Stoichiometry
It is the quantitative relationship between reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
Based on the balanced equation, it helps in calculating:
- Mass of reactants/products
- Volume of gases
- Number of moles or particles
Example:
From the equation:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
- 2 moles H₂ react with 1 mole O₂ to give 2 moles H₂O
- 4 g H₂ reacts with 32 g O₂ to give 36 g H₂O
Limiting Reagent
In a chemical reaction, the reactant that is completely used up first and limits the amount of product formed is called the limiting reagent.
Steps to Identify Limiting Reagent:
- Convert given masses to moles.
- Divide by the respective stoichiometric coefficients.
- The smaller value identifies the limiting reagent.
Example:
If 4 g H₂ and 32 g O₂ are given:
2H₂ + O₂ → 2H₂O
- 4 g H₂ = 2 moles
- 32 g O₂ = 1 mole
- As per the equation: 2 mol H₂ reacts with 1 mol O₂
- Both are in exact proportion → No limiting reagent
Practice Questions
- Define empirical and molecular formula. How are they related?
- Calculate the number of molecules in 2 moles of CO₂.
- Write and balance the reaction between Na and H₂O.
- What is meant by limiting reagent? Explain with an example.
- What is the volume occupied by 3 moles of a gas at STP?
Basic Accounting Terms Class 11 Notes
Basic Accounting Terms – Class 11 Notes
Chapter 2 of Class 11 Accountancy covers the essential terms used in accounting. These terms form the foundation of financial literacy for commerce students.
1. Entity
An entity is an independent economic unit that carries out business activities. It can be a person, firm, or company.
Example: Tata Motors, Infosys, or a small shop near your home.
2. Business Transaction
A business transaction is any financial activity that affects the financial position of a business and can be measured in money terms.
Example: Buying goods for ₹5,000 or selling services worth ₹2,000.
3. Capital
Capital is the amount invested by the owner into the business. It could be in the form of cash or assets and is considered a liability of the business to the owner.
Example: If Ramesh starts a business and invests ₹1,00,000, that becomes his capital.
4. Drawings
Drawings refer to the amount withdrawn by the owner from the business for personal use.
Example: If the owner buys a bike for himself using business money, it is called a drawing.
5. Liabilities
Liabilities are the obligations that a business needs to repay in the future.
Types of Liabilities
i) Current Liabilities: Payable within one year.
Example: Creditors, Bills Payable.
ii) Non-Current Liabilities: Payable after one year.
Example: Bank Loans, Debentures.
6. Assets
Assets are valuable resources owned by a business to generate income.
Types of Assets
i) Current Assets: Realized within a year.
Example: Cash, Debtors, Stock.
ii) Non-Current Assets: Held for long-term business use.
Example: Land, Machinery.
Subtypes:
a) Tangible Assets: Physical existence (e.g., Building).
b) Intangible Assets: No physical existence (e.g., Goodwill, Patent).
7. Expenses
Expenses are the costs incurred to earn revenue.
Example: Salaries, Rent, Wages.
8. Expenditure
Expenditure is the amount spent on acquiring goods or services.
i) Revenue Expenditure: Benefit lasts less than a year.
Example: Utility bills, Interest.
ii) Capital Expenditure: Benefit lasts more than a year.
Example: Buying machinery.
9. Revenue
Revenue is the total income earned through business activities.
Example: Sales, Commission earned, Rent received.
10. Income
Income = Revenue – Expenses. It is the net increase in business wealth.
11. Profit
Profit is when revenue exceeds expenses in a financial year.
Formula: Profit = Revenue – Expenses
12. Gain
Gain is a non-recurring profit from events not part of core business.
Example: Selling an old computer for ₹8,000 when its book value is ₹5,000.
13. Loss
Loss is when expenses exceed revenues.
Formula: Loss = Expenses – Revenue
14. Goods
Goods are items purchased for resale, not for personal use.
Example: A stationery shop purchases pens and sells them to customers.
15. Purchases
Purchases are goods bought for resale (trading) or for production (manufacturing).
16. Purchase Return
Purchase Return refers to returning previously bought goods to the supplier.
17. Sales
Sales are the revenue from goods/services provided to customers.
18. Sales Return
Sales Return is when customers return goods to the business due to defects or mismatch.
19. Stock
Stock is the unsold goods lying with the business on a particular date.
20. Debtors
Debtors are customers who bought goods on credit and are yet to pay.
21. Creditors
Creditors are those from whom the business has bought goods/services on credit.
22. Voucher
Voucher is a document that proves a business transaction occurred.
Example: Receipt, Invoice, Cash Memo.
23. Discount
Discount is a reduction in price offered by the seller.
i) Trade Discount: Given to boost sales; not recorded in books.
ii) Cash Discount: Given to encourage timely payment; recorded in books.
24. Bad Debts
Bad Debts are unrecoverable amounts from debtors, written off as loss.
25. Operating Cycle
The operating cycle is the time between acquiring an asset and converting it into cash.
Practice Questions – Basic Accounting Terms Class 11
Q1. What is the difference between capital and revenue expenditure?
Q2. Give two examples each of current and non-current assets.
Q3. What is the meaning of drawings? Give a practical example.
Q4. Define the term ‘Voucher’ and explain its types with examples.
Q5. Distinguish between creditors and debtors.
These questions will help you prepare well for Basic Accounting Terms Class 11 Important Questions and CBSE board exams.
Class 11 Accounts Chapter – 1 Notes
CBSE Class 11 Accountancy – Chapter 1: Introduction to Accounting Notes
Learning Objectives
- Understand the meaning, significance, objectives, advantages, and limitations of accounting.
- Identify the users of accounting information and understand their needs in decision making.
- Learn various terms used in accounting and differentiate between closely related concepts.
What is Accounting?
All business entities need to know:
- Whether they are earning profits or facing losses
- The total amount payable and receivable
- The total purchases, sales, and expenses during an accounting period
Maintaining a complete and systematic record of every business transaction helps in understanding the financial position, assessing income tax and GST.
Definition by AICPA: “Accounting is the art of recording, classifying, and summarizing in a significant manner and in terms of money, transactions and events which are, in part at least, of a financial character, and interpreting the results thereof.”
Definition by Accounting Principles Board (APB): “Accounting is a service activity. Its function is to provide quantitative information, primarily financial in nature, about economic entities that is intended to be useful in making economic decisions.”
Defination of Accounting
Accounting is the process of identifying, recording, classifying, summarizing, interpreting, and communicating financial information to users for effective decision making.
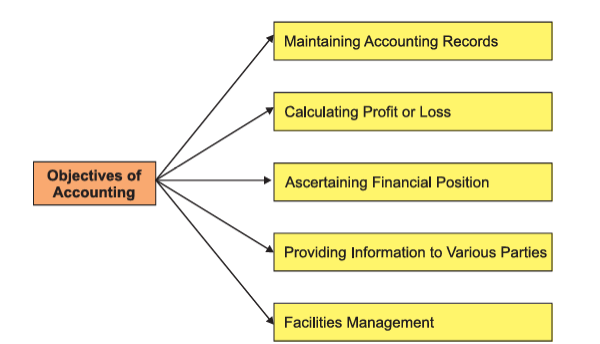
Objectives of Accounting
- Maintaining Accounting Records: To record all business transactions systematically and completely.
- Calculating Profit or Loss: To ascertain net profit or loss during an accounting period.
- Ascertaining Financial Position: Done through the Balance Sheet, which lists Assets, Liabilities, and Capital.
- Providing Information to Stakeholders: Useful to owners, investors, employees, banks, and government.
- Facilitating Management: Helps in decision making, budgeting, and forecasting.
Advantages of Accounting
- Assists management in making economic decisions.
- Helps compare current results with previous years.
- Reveals financial position through the Balance Sheet.
- Records transactions in a systematic and legal manner.
- Facilitates accurate tax assessment including Income Tax and GST.
- Helps in setting appropriate pricing strategies.
Limitations of Accounting
- Historical in nature: Does not reflect the current value or price level changes.
- Ignores qualitative aspects: Such as staff quality, customer satisfaction, and management efficiency.
- Prone to Window Dressing: Manipulating accounts to present a better image.
- Subjective judgments: Like estimating asset life or doubtful debts.
- Conventional Limitations: Assets are shown at historical cost, not at market value.
Book keeping vs Accounting
| Basis | Bookkeeping | Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Recording transactions of financial nature | Includes bookkeeping + Summarizing, Interpreting, Reporting |
| Stage | Primary | Secondary |
| Objective | To maintain systematic records | To find net results & communicate financial data |
| Nature of Work | Routine and Clerical | Analytical and Interpretative |
Types of Accounting Information
- Income Statement: Shows net profit or loss.
- Balance Sheet: Depicts assets, liabilities, and capital.
- Schedules & Notes: Provide additional detail to financial statements.
Qualitative Characteristics of Accounting Information
- Reliability: Based on verified and factual documents, free from bias.
- Relevance: Must help in making informed decisions.
- Understandability: Presented clearly for users to comprehend.
- Comparability: Must allow comparison across time periods and firms.
Role of Accounting in Business
- Language of Business: Communicates financial health of business.
- Historical Record Keeper: Maintains chronological records.
- Information System: Records all financially relevant events.
- Service Provider: Delivers financial data to stakeholders.
- Statutory Compliance: Ensures adherence to tax laws and business regulations.