Class – 9 CBSE
Chapter – Motion
Class 9 Physics Chapter 1 notes
- Motion:
An object is said to be in motion if it changes its position with respect to its surroundings.
Example: A car moving on the road or a fan rotating. - Rest:
A body is at rest if it does not change its position with respect to its surroundings.
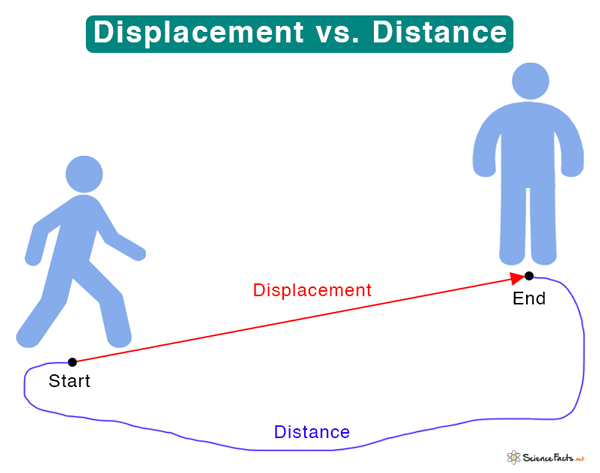
Example: A book lying on a table. - Displacement:
The shortest distance between the initial and final positions of an object.
SI Unit: metre (m)
Example: If you walk from your home to a friend’s house in a straight line, that’s displacement.
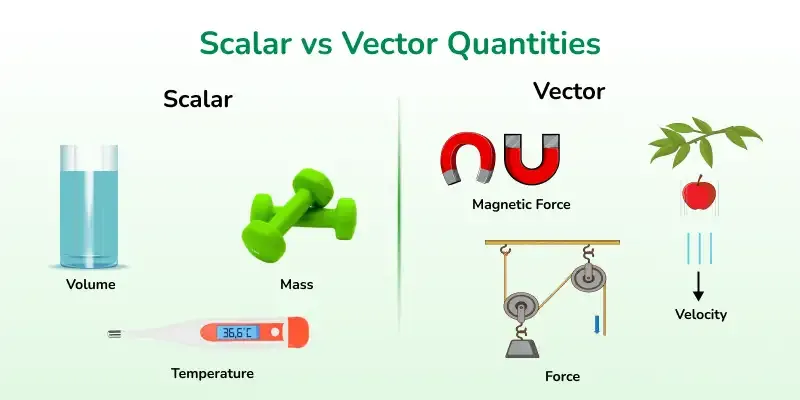
- Vector:
Physical quantities having both magnitude and direction.
Example: Velocity, force. - Scalar:
Physical quantities having only magnitude and no direction.
Example: Speed, distance, time.
- Uniform Motion:
A body covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
Example: A car moving at a constant speed of 60 km/h on a highway. - Non-uniform Motion:
A body covers unequal distances in equal time intervals or equal distances in unequal time intervals.
Example: A car stuck in traffic keeps changing speed.

- Speed:
Speed = Distance / Time
SI Unit: m/s
Example: A train covers 300 km in 3 hours, so speed = 100 km/h. - Average Speed:
Average Speed = Total Distance Travelled / Total Time Taken - Locomotion:
Movement of animals from one place to another.
Example: A dog running, a bird flying. - Velocity:
The displacement covered per unit time in a given direction.
Velocity = Displacement / Time
SI Unit = m/s - Uniform Velocity:
Equal displacement in equal intervals of time in a particular direction. - Variable Velocity:
Displacement changes in unequal intervals of time or direction keeps changing.
Example: A bus moving in a city street with turns and stops. - Acceleration:
Rate of change of velocity.
Acceleration = (Final Velocity – Initial Velocity) / Time
SI Unit = m/s² - Retardation or Deceleration:
Negative acceleration; when the velocity of an object decreases.
Example: A bicycle slowing down before stopping. - Uniform Acceleration:
Velocity changes by equal amounts in equal intervals of time.
Example: Free fall under gravity. - Variable Acceleration:
Velocity changes by unequal amounts in equal time intervals.
Example: A car speeding up irregularly in traffic.
Equations of Motion (For Uniform Acceleration)
- v = u + at
- s = ut + ½ at²
- v² = u² + 2as
Where:
- s = Distance
- u = Initial velocity
- v = Final velocity
- a = Acceleration
- t = Time
Graphs
- Distance-Time Graph:
-
- Shows time vs distance.
- Slope = Speed
Example: A straight line shows uniform speed.
- Velocity-Time Graph:
-
- Shows time vs velocity.
- Slope = Acceleration
- Area under the graph = Distance covered
Circular Motion Concepts
- Uniform Circular Motion:
When a body moves in a circular path with uniform speed.
Example: A satellite orbiting the Earth. - Angular Displacement:
Angle swept by the radius of a circular path in a given time. - Angular Velocity (ω):
Angular Velocity = Angle swept / Time = θ / t
Units: rad/s - Time Period (T):
Time taken to complete one full revolution. - Frequency (f):
Number of revolutions per unit time.
f = 1 / T
Relation Between Linear and Circular Motion
- Linear Velocity (v):
v = 2πr / T = rω - Relation Between Linear Velocity and Time Period:
v = Circumference / Time period
Notations of Physical Quantities
| Quantity | Symbol |
| Distance | s |
| Speed | v |
| Time | t |
| Acceleration | a |
| Initial Velocity | u |
| Final Velocity | v |
| Average Velocity | v̅ |
Useful Formulas and Equations
- v = u + at
- s = ut + ½ at²
- v² = u² + 2as
- Average Velocity (v̅) = (u + v) / 2
- s = v̅ × t = [(u + v)/2] × t
.
